
Texas Instruments CC1310 SimpleLink Ultra-Low Power Wireless MCUs
Texas Instruments CC1310 SimpleLink™ Ultra-Low Power Wireless Microcontrollers are a cost-effective, ultra-low power sub-1GHz RF device. It combines a flexible, very low power RF transceiver with a powerful 48MHz Cortex-M3 microcontroller in a platform supporting multiple physical layers and RF standards. A dedicated Radio Controller (Cortex-M0) handles low-level RF protocol commands that are stored in ROM or RAM, thus ensuring ultra-low power and flexibility. The low-power consumption of the CC1310 device does not come at the expense of RF performance; the CC1310 device has excellent sensitivity and robustness (selectivity and blocking) performance. The very low active RF, MCU current, and low-power mode current consumption provide excellent battery lifetime and allow operation on small coin-cell batteries and in energy-harvesting applications.Features
- Microcontroller
- Powerful ARM® Cortex®-M3
- EEMBC CoreMark® score: 142
- EEMBC ULPBench™ score: 158
- Up to 48MHz clock speed
- 128KB of In-system programmable flash
- 8KB of SRAM for cache (or as general-purpose RAM)
- 20KB of ultralow leakage SRAM
- 2-Pin cJTAG and JTAG debugging
- Supports Over-the-Air Upgrade (OTA)
- Ultralow power sensor controller
- Can run autonomous from the rest of the system
- 16-Bit Architecture
- 2KB of Ultralow leakage SRAM for code and data
- Efficient code-size architecture, placing TI-RTOS, drivers and bootloader in ROM
- RoHS-compliant package
- 7mm×7mm RGZ VQFN48 (30 GPIOs)
- 5mm×5mm RHB VQFN48 (15 GPIOs)
- 4mm×4mm RSM VQFN48 (10 GPIOs)
- Peripherals
- All digital peripheral pins can be routed to any GPIO
- Four general-purpose timer modules (eight 16-Bit or four 32-Bit timers, PWM each)
- 12-Bit ADC, 200 ksamples/s, 8-channel analog MUX
- Continuous time comparator
- Ultra-low power clocked comparator
- Programmable current source
- UART
- 2× SSI (SPI, MICROWIRE, TI)
- I2C
- I2S
- Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- AES-128 Security module
- True Random Number Generator (TRNG)
- Support for eight capacitive sensing buttons
- Integrated Temperature Sensor
- External system on-chip internal DC-DC converter
- Very few external components
- Seamless integration with the simpleLink CC1190 range extender
- Low Power
- 1.8 to 3.8V Wide supply voltage range
- 5.5mA Active-Mode RX
- 12.9mA Active-Mode TX at +10dBm
- 2.5mA (51µA/MHz) Active-mode MCU 48MHz running coremark
- 48.5CoreMark/mA Active-Mode MCU
- Active-mode sensor controller at 24MHz: 0.4mA + 8.2µA/MHz
- 0.85µA Sensor controller, one wake up every second performing one 12-Bit ADC sampling
- 0.6µA Standby (RTC running and RAM and CPU retention)
- 185nA Shutdown (wakeup on external events)
- RF Section
- Excellent receiver sensitivity -124dBm using long-range mode, -110dBm at 50kbps
- 52dB Excellent selectivity
- 90dB Excellent blocking performance
- Programmable output power up to +14dBm
- Single-ended or differential RF interface
- Suitable for systems targeting compliance with worldwide radio frequency regulations
- ETSI EN 300 220, EN 303 131, EN 303 204 (Europe)
- FCC CFR47 Part 15 (US)
- ARIB STD-T108 (Japan)
- Wireless M-Bus and IEEE 802.15.4g PHY
- Tools and development environment
- Full-feature and low-cost development kits
- Multiple reference designs for different RF configurations
- Packet Sniffer PC Software
- Sensor Controller Studio
- SmartRF™ Studio
- SmartRF Flash Programmer 2
- IAR Embedded Workbench® for ARM
- Code Composer Studio™
Applications
- 315, 433, 470, 500, 779, 868, 915, and 920MHz ISM and SRD systems
- Low-power wireless systems with 50kHz to 5MHz channel spacing
- SmartGrid and automatic meter reading
- Home and building automation
- Wireless alarm and security systems
- Industrial monitoring and control
- Wireless healthcare applications
- Wireless sensor networks
- Active RFID
- IEEE 802.15.4g, IP-enabled smart objects (6LoWPAN), wireless M-Bus, KNX systems, Wi-SUN, ZigBee and proprietary systems
- Energy harvesting applications
- ESL (Electronic Shelf Label)
- Long-range sensor applications
- Heat cost allocators
Videos
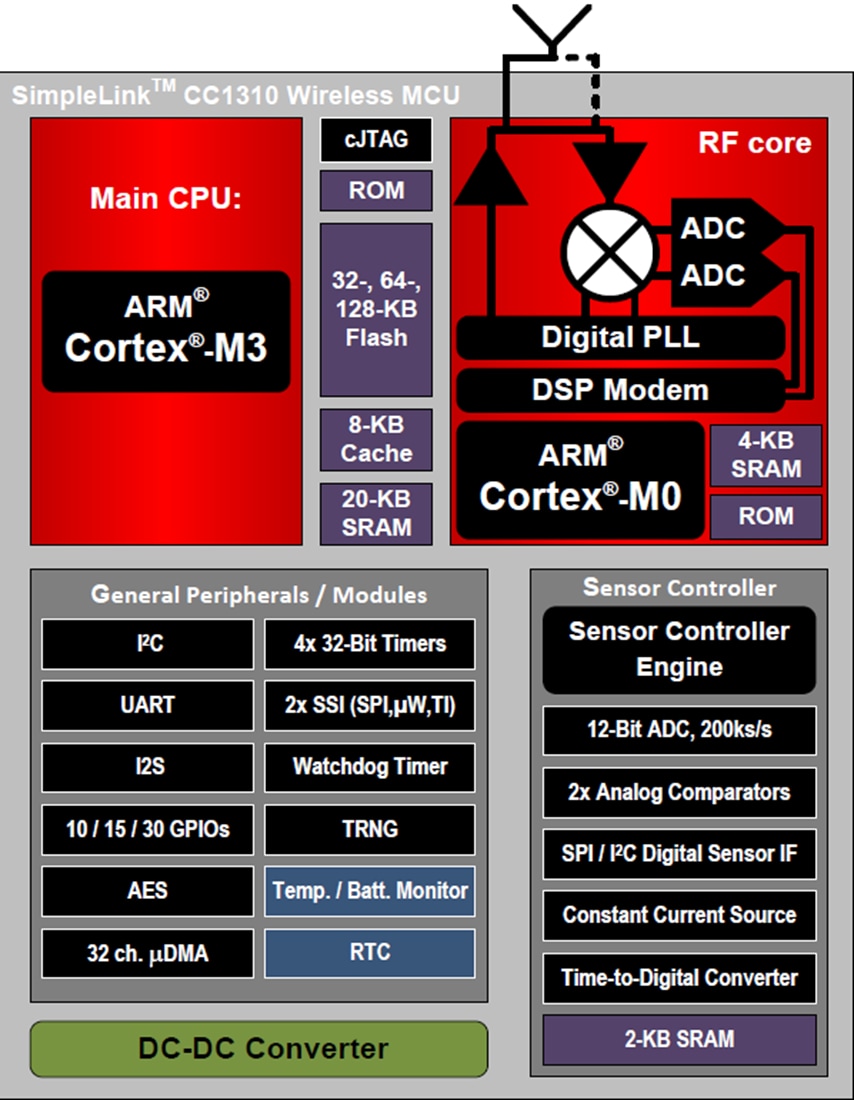
Functional Block Diagram
Publicado: 2015-11-12
| Actualizado: 2022-03-11









